Glue is manufactured by combining various chemicals and substances to create an adhesive substance. The process involves mixing and heating the ingredients until they are liquefied, then cooling and shaping the mixture into the desired form.
Glue is a type of adhesive substance that is widely used in many industries and applications. It can be used to bond materials together, seal gaps and cracks, and even as a coating material.
The manufacturing process of glue involves combining different chemicals and substances, such as polymers, resins, and solvents, to create a sticky and durable adhesive. The mixture is heated to a liquid state and then cooled and shaped into the desired form, such as a liquid, gel, or solid.
The resulting product can vary in properties, such as strength, viscosity, and drying time, depending on the specific ingredients and manufacturing process used. Glue is an essential component in many products and industries, from woodworking and construction to automotive and aerospace.
Contents
The Sticky Beginnings
Historical Adhesives
Early civilizations used natural materials like beeswax and tree sap for bonding.
Ancient Egyptians employed glue made from animal hides and bones for construction.
Modern Glue Evolution
Today’s adhesives are a blend of synthetic polymers and additives for various applications.
High-performance glues are engineered to bond diverse materials with precision.

Ingredients That Stick
When it comes to the process of manufacturing glue, the ingredients used play a critical role in determining its adhesive properties. Let’s explore the diverse world of materials that contribute to the stickiness of glue, from natural sources to synthetic compounds.
Natural Sources
The production of glue often harnesses the adhesive qualities of natural sources, such as animal proteins and plant-based substances. These materials, including collagen, casein, and cellulose, are extracted and processed to create adhesives that are widely used in various industries.
Synthetic Compounds
In addition to natural sources, synthetic compounds play a crucial role in adhesive manufacturing. These synthetic materials, such as polyvinyl acetate (PVA), acrylic polymers, and cyanoacrylate, are engineered to exhibit superior adhesive properties, offering versatility and reliability in bonding different materials.
Types Of Glue
Glue is manufactured through a complex process that involves combining various ingredients such as polymers, solvents, and additives.
These materials are carefully mixed, heated, and cooled to create different types of glue, including adhesive tapes, liquid glues, and hot melt adhesives. The manufacturing process ensures that the glue is strong, durable, and suitable for different applications.
Water-based Adhesives
Water-based adhesives are eco-friendly and safe for indoor use.
Solvent-based Solutions
Solvent-based glues offer strong bonding properties for various materials.
Hot Melt Glues
Hot melt glues provide quick adhesion and are commonly used in packaging.
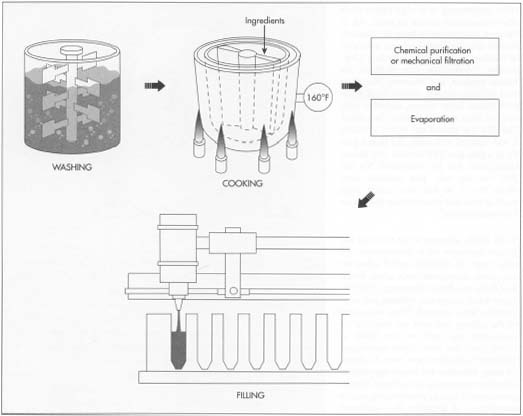
The Manufacturing Process
Glue is manufactured by mixing various chemicals together in a controlled environment. The process involves blending and heating the components to create a viscous liquid that can be used for bonding different materials.
Additional steps may be taken to improve the adhesive’s properties, such as adjusting the pH level or adding stabilizers.
Preparation Of Raw Materials
In the manufacturing process of glue, the first step is the preparation of raw materials. Various components are required to create a strong adhesive. These components include polymers, resins, solvents, and additives.
Polymers and resins serve as the primary bonding agents, while solvents help in maintaining the desired consistency of the glue. Additives are used to enhance specific properties of the adhesive, such as drying time or flexibility.
To prepare the raw materials, polymers and resins are carefully selected based on their properties and intended application. Solvents and additives are chosen to complement the desired characteristics of the glue.
The raw materials are then measured and weighed according to specific formulations to ensure consistency and quality in the final product. This precise preparation of raw materials is crucial in creating a reliable and effective adhesive.
Mixing And Reacting
Once the raw materials are prepared, the next step in the manufacturing process is mixing and reacting. This stage involves combining the polymers, resins, solvents, and additives in carefully controlled proportions.
The mixing process can be performed using various methods, such as mechanical mixing or chemical reactions. During mixing, the raw materials are blended together to form a homogeneous mixture.
This ensures that all components are evenly distributed, resulting in a uniform adhesive with consistent properties. The mixture may undergo chemical reactions, such as polymerization, which further enhance the bonding capabilities of the glue.
Refining And Purifying
After the mixing and reacting stage, the adhesive mixture may undergo refining and purifying processes. These processes are essential to remove any impurities or unwanted substances that could affect the quality and performance of the glue.
Refining involves filtering the mixture to remove any solid particles or contaminants. This step ensures a smooth and clean adhesive, free from any debris that could interfere with its bonding properties.
Purifying, on the other hand, focuses on removing excess solvents or other volatile components. This helps in achieving the desired consistency and stability of the glue.
Once the refining and purifying processes are complete, the glue is ready for packaging and distribution. The manufacturing process ensures that the adhesive meets stringent quality standards, providing users with a reliable and effective bonding solution.
Quality Control Measures
Quality control is an essential aspect of glue manufacturing, ensuring that the end product meets the required standards for adhesion, consistency, and safety. In this article, we will discuss the various quality control measures involved in glue production.
Testing For Adhesion
One of the critical quality control measures in glue manufacturing is testing for adhesion. Adhesion is the ability of the glue to stick to a surface, and it is essential to ensure that the glue bonds appropriately to the intended surface.
Manufacturers test adhesion by applying the glue to different surfaces, such as metal, plastic, and wood, to ensure that the glue’s adhesion strength is consistent across various surfaces.
Consistency Checks
Another essential quality control measure in glue manufacturing is consistency checks. Consistency is crucial to ensure that the glue’s properties are the same from batch to batch, as any deviation from the standard can affect the glue’s performance.
Manufacturers perform consistency checks by measuring the viscosity, pH, and solids content of the glue to ensure that they fall within the required range.
Safety Standards
Ensuring safety is an essential quality control measure in glue manufacturing, as the production process involves the use of hazardous chemicals.
Manufacturers must adhere to strict safety standards to ensure the safety of their workers and the environment. Safety measures include proper labeling, handling, and disposal of chemicals, as well as providing protective gear for workers.
| Quality Control Measures | Description |
|---|---|
| Testing for Adhesion | Testing the glue’s ability to stick to different surfaces to ensure consistent adhesion strength. |
| Consistency Checks | Measuring the viscosity, pH, and solids content of the glue to ensure consistency across batches. |
| Safety Standards | Adhering to strict safety standards to ensure the safety of workers and the environment. |
- Glue manufacturing requires strict quality control measures to ensure the end product’s performance.
- Testing for adhesion, consistency checks, and safety standards are essential quality control measures in glue manufacturing.
- Manufacturers test adhesion by applying the glue to different surfaces to ensure consistent adhesion strength.
- Consistency checks involve measuring the viscosity, pH, and solids content of the glue to ensure consistency across batches.
- Safety standards include proper labeling, handling, and disposal of chemicals, as well as providing protective gear for workers.
Packaging The Stickiness
Once the glue manufacturing process is complete, the next crucial step is packaging the adhesive in a way that ensures its effectiveness and convenience for users.
Proper container selection, filling and sealing, as well as labeling guidelines, play a significant role in maintaining the quality and usability of the glue. In this section, we will explore each of these aspects in detail.
Container Selection
Choosing the right container is vital to preserve the stickiness and shelf life of the glue. Manufacturers often opt for containers made of materials such as plastic, glass, or metal, depending on the type of glue being packaged.
Here are some key factors to consider when selecting containers:
- Durability: The container must be sturdy enough to withstand any external pressure or impact during transportation and storage.
- Chemical Compatibility: Glue can have different compositions, so it is essential to choose a container material that is resistant to the adhesive’s chemical properties.
- Airtight Seal: To prevent the glue from drying out, the container should have a tight seal that prevents air from entering and moisture from escaping.
- Easy Dispensing: Consider the ease of dispensing the glue from the container, as it affects user experience and convenience.
Filling And Sealing
Once the appropriate containers are selected, the glue is filled into them using specialized equipment. The filling and sealing process must be carefully executed to ensure the glue remains intact and usable.
Here are the key steps involved:
- Preparation: The containers are thoroughly cleaned and sanitized to eliminate any contaminants that could compromise the glue’s quality.
- Accurate Measurement: The glue is precisely measured to ensure consistent volumes in each container, avoiding any inconsistencies in stickiness.
- Filling: The measured glue is carefully poured or injected into the containers, taking care not to introduce air bubbles that could affect the adhesive’s effectiveness.
- Sealing: After filling, the containers are sealed tightly to maintain the glue’s freshness and prevent leakage. Different sealing methods such as capping, heat sealing, or induction sealing may be used depending on the container type and adhesive properties.
Labeling Guidelines
Proper labeling is crucial for providing essential information about the glue and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
Here are some guidelines for effective labeling:
- Product Information: The label should include the adhesive’s brand name, type, and any specific instructions or warnings for safe usage.
- Ingredients: It is essential to list the glue’s ingredients to inform users of any potential allergens or harmful substances.
- Batch Number: Each container should have a unique batch number for traceability and quality control purposes.
- Barcodes and QR Codes: Including barcodes or QR codes on labels can streamline inventory management and provide easy access to additional product information.
By adhering to proper container selection, filling and sealing techniques, and labeling guidelines, glue manufacturers ensure that the stickiness is preserved and the glue is packaged in a user-friendly manner.
These steps contribute to the overall quality and usability of the adhesive, meeting the needs of both professionals and DIY enthusiasts alike.
Environmental Considerations
When manufacturing glue, it’s crucial to consider the environmental impact. By utilizing eco-friendly ingredients, focusing on sustainable manufacturing, and establishing effective recycling and disposal methods, the glue production process can minimize its ecological footprint.
Eco-friendly Ingredients
Glue manufacturers are increasingly turning to biodegradable and renewable ingredients to reduce the environmental impact. This shift toward organic materials not only lessens the reliance on non-renewable resources but also contributes to the overall reduction in carbon emissions.
Sustainable Manufacturing
Adopting energy-efficient production techniques and implementing waste reduction measures are integral to sustainable glue manufacturing. By optimizing resource usage and minimizing pollutant emissions, manufacturers can operate in a more environmentally responsible manner.
Recycling And Disposal
Proper disposal and recycling processes play a vital role in reducing the environmental impact of glue manufacturing. Developing recycling programs for unused materials and establishing safe disposal methods for waste products ensure that the environmental impact is minimized throughout the product lifecycle.
Innovations In Glue Manufacturing
Innovations in glue manufacturing have revolutionized the adhesive industry, leading to the development of smart adhesives, biodegradable options, and the future of adhesion technology.
Smart Adhesives
Smart adhesives are a result of cutting-edge innovations in glue manufacturing. These adhesives are designed to react to environmental stimuli, allowing for self-healing and self-monitoring properties. They are engineered to provide enhanced performance and durability in various applications.
Biodegradable Options
The demand for eco-friendly adhesives has led to the development of biodegradable options. These adhesives are made from sustainable raw materials and are designed to decompose naturally, reducing environmental impact.
Manufacturers are continually exploring new biomaterials and biopolymers to create adhesives with renewable and biodegradable properties.
Future Of Adhesion Technology
The future of adhesion technology is driven by ongoing research and development efforts. Advancements in nanotechnology, nanocomposites, and microscopic structures are shaping the next generation of adhesives.
These innovations aim to enhance bonding strength, reduce environmental impact, and expand the capabilities of adhesives in high-tech industries.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are The Raw Materials For Making Glue?
The raw materials for making glue include natural substances like animal hide, bones, and fish. Synthetic glues are made from chemicals like polyvinyl acetate (PVA) and ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA).
What Is Glue Actually Made Of?
Glue is typically made of polymers, resins, and additives that create a strong adhesive bond.
How Is Elmer’s Glue Manufactured?
Elmer’s glue is manufactured by mixing water, polyvinyl acetate, and other additives. The mixture is heated and stirred to create the glue. The final product is then tested for quality and packaged for distribution.
How Do You Make Glue?
To make glue, mix water with a natural adhesive like animal collagen or plant starch. Heat and stir the mixture until it thickens.
Conclusion
The manufacturing process of glue involves blending raw materials and applying heat. The resulting adhesive product is then packaged for distribution.
Understanding how glue is made provides insight into its versatility and importance across various industries. This knowledge enhances appreciation for the role of glue in everyday life.

